Actinonin is a naturally occurring antibacterial agent that has demonstrated anti-tumor activity. The natural product peptidimetic actinonin demonstrates antiproliferative, antiangiogenic, and antimetastatic properties against many human cancers, including leukemia and lymphoma, as well as against lung and prostate tumors, both in vitro and in vivo.
Actinonin is a naturally occurring antibacterial agent that has demonstrated anti-tumor activity. The natural product peptidimetic actinonin demonstrates antiproliferative, antiangiogenic, and antimetastatic properties against many human cancers, including leukemia and lymphoma, as well as against lung and prostate tumors, both in vitro and in vivo. An improved method for the asymmetric synthesis of (S,S,R)-(-)-actinonin allows for inexpensive and abundant production of this compound and novel analogs. Actinonin and actinonin analogs were assayed for cytotoxity in human prostate, lymphoma, and acute myeloid leukemia cells. Actinonin and some of its analogs are remarkably cytotoxic in the µM range against all the cancer cell lines tested. 1. Antitumor Activity in Vitro and in Vivo. Actinonin, an antibiotic and CD13/aminopeptidase N(APN) inhibitor, has been shown to be cytotoxic to tumor cell lines in vitro. Actinonin inhibited growth of NB4 and HL6O human cell lines and AKR mouse leukemia cells in vitro with an IC50 of about 2-5 mg/ml. The inhibitory effect on CD13-positive cells was not blocked by pretreatment with the anti-CD13/APN monoclonal antibody F23, which binds with high affinity to the active site of CD13/APN and blocks its enzymatic activity. Moreover, F23 alone was not inhibitory to CD13-positive cells. Furthermore, a similar inhibitory IC50 of actinonin was seen in the CD13-negative cell lines RA.JI and DAUDI human lymphoma. These data suggest that the inhibitory effect of actinonin is not mediated by inhibition of CD13/APN. Cell cycle analysis showed that actinonin induces a G1 arrest in HL6O and NB4 cells; apoptosis was observed in 20-35% of the cells as measured by intracellular flow cytometry. To assess whether these effects could be seen in vivo, the effect of actinonin on the syngeneic AKR mouse leukemia model was evaluated. Actinonin showed dose-dependent antitumor effects on AKR leukemia in vivo, resulting in a survival advantage. In conclusion, apoptosis, growth inhibition, and therapeutic effects in vivo are induced by actinonin and are not likely to be mediated by CD13/APN.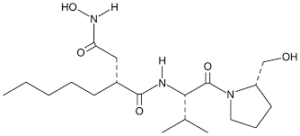
Figure 1. The chemical structure of Actinonin.