The method of detergent removal can be an important consideration. If dialysis is to be employed, a detergent with a high CMC is clearly preferred. Alternatively, if ion exchange chromatography is utilized, a non-ionic detergent (e.g. n-Octyl-β-D-Glucopyranoside, OG, O-1036 see structure,OCTYL-GLUCOSIDE DDM, D-1304) or a sulfobetaines.
9 Tips for Selecting a Biological Detergent
 1. The first step is a survey of the scientific literature, e.g. Highwire or Pubmed. A detergent that has been used previously for the isolation and characterization of a protein with similar biochemical or enzymological properties should be tried first.
2. Solubility of the detergent at working temperature should be another consideration. For example, Sulfobetaine-14 is insoluble in water at +4°C.
1. The first step is a survey of the scientific literature, e.g. Highwire or Pubmed. A detergent that has been used previously for the isolation and characterization of a protein with similar biochemical or enzymological properties should be tried first.
2. Solubility of the detergent at working temperature should be another consideration. For example, Sulfobetaine-14 is insoluble in water at +4°C.
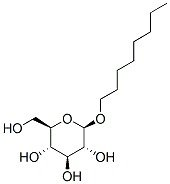
3. The method of detergent removal can be an important consideration. If dialysis is to be employed, a detergent with a high CMC is clearly preferred. Alternatively, if ion exchange chromatography is utilized, a non-ionic detergent is the detergent of choice. 4. Preservation of enzymological activity may require experimenting with several detergents. Not only the type but also the quantity of the detergent used will affect the activity of the protein. Proteins biological activity is preserved over a very narrow range of concentration of detergent. Below this range the protein is not solubilized and above a particular concentration, the protein is inactivated. 5. Since Protein Solubilizer X-100 contains aromatic rings that absorb at 260-280 nm, this detergent should be avoided if the protocols require UV monitoring of protein concentration. Similarly, ionic detergents should be avoided if the proteins are to be separated by isoelectric focusing. For gel filtration of proteins, detergents with smaller aggregation numbers should be considered. 6. Detergents of highest purity should be used since some detergents such as Protein Solubilizer X-100 are generally known to contain peroxides as contaminants. All of AG Scientific's series of protein solubilizers are tested to minimize aldehyde (< 0.1 mM), peroxides (< 0.1 mM) and conductivity (< 5 mhos). 7. A non-toxic detergent should be preferred over a toxic one. For example, digitonin, is used as a detergent because it effectively water-solubilizes . However it is also a cardiac glycoside and must be handled with special precaution.
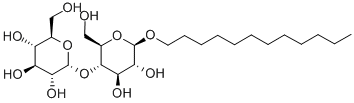
8. Specific detergents often work better for particular isolation procedures. For example, n-Dodecyl-Beta-D-maltopyranoside has been found to be the detergent of choice for the isolation of cytochrome c oxidase. Hence, experimentation may be required for determining optimal conditions for isolation of a membrane protein in its biologically active form. 9. It has been observed that the inclusion of non-detergent sulfobetaines (NDSBS), e.g.NBSB-195, NBSB-201, NBSB-201, NDSB-256 with detergents in the isolation buffer dramatically improves yields of solubilized membrane proteins.
