As a core structure in many antibiotics, the beta-lactam ring is a cyclic amide. Beta-lactam antibiotics almost universally inhibit bacterial cell wall synthesis and thus induce the destruction of bacterial cells. Bacteria have evolved an enzyme that combats this antibiotic and increases resistance to death induced by antibiotics: the beta-lactamase enzyme. Beta-lactamase enzymes can be used in a multitude of antibiotic and bacterial resistance studies. Below are a few frequently asked questions about this bacterial enzyme.
What is Beta-Lactamase?
Beta lactamases are enzymes found in the plasmid of bacterial cells to help boost survivability. Targeting the beta lactam 4-member ring, beta lactamases destroy the structure via hydrolysis. Penicillinase, a specific type of beta lactamase, acts specifically on penicillins and was the first beta lactamase enzyme to be discovered from gram-negative E. coli. Natural selection favored bacteria that developed a resistance to penicillin, and there is now widespread resistance to penicillinase.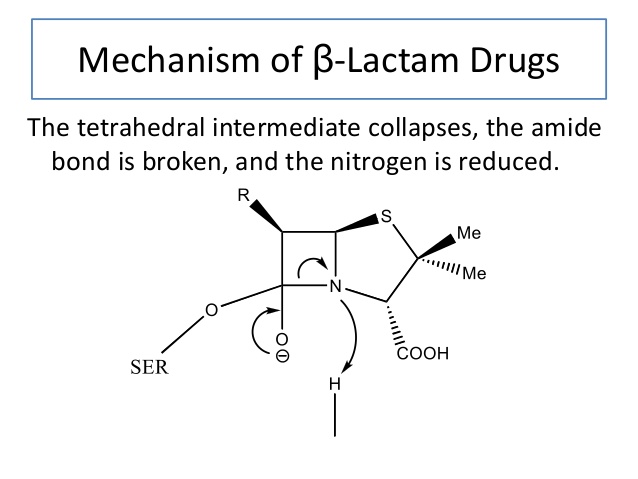
How does Beta Lactamase boost bacterial cellular resistance?
Beta-lactam is a class of antibiotics of which target the 5-glycine crosslinking bridges in the cell walls of bacteria, thus weakening the cell wall. Beta lactamase destroys the 4-member ring antibiotic, preventing transpeptidase (PBP) to be bound by beta lactam, thus inhibiting the interruption of the 5-glycine bridge.What are the classifications of Beta-Lactamase?
Currently, there are two schemes of which beta-lactamase is classified: the molecular classification scheme and the functional classification scheme. The molecular classification uses amino acid sequences to sort the enzymes into class A, C, and D, while class B classification solely depends on divalent zinc ions to perform substrate hydrolysis. Functional classification of beta-lactamase is based upon substrate and inhibitor profiles in a more phenotypical type of sorting.How can an assay measuring the activity of beta lactamase be performed?
For rapid beta-lactamase detection in a cost-efficient manner, nitrocefin is recommended. Nitrocefin, being a chromogenic cephalosporin substrate, is routinely used for beta lactamase detection. PCR can also be used for beta-lactamase detection as well, but is not as cost-efficient.Is there way to identify an inhibitor that stops beta-lactamase production even in the presence of penicillin?
"I have a bacteria strain that produces beta-lactamase of which grows normally in the presence of penicillin and in the presence of an unknown substance, but its growth is inhibited when penicillin and the unknown substance is mixed together. How can I identify an inhibitor that stops beta-lactamase production in the presence of penicillin?"Each class of beta-lactamase is susceptible to different inhibitors. By using the identity of the beta-lactamase enzyme class that is normally found within the bacteria, the substance of which acts as an inhibitor can be narrowed down and identified with further testing. The two compounds (the unknown substance and penicillin) may also produce a different effect on beta-lactamase expression as well when combined together.
How do I know if my substance is a beta-lactamase inhibitor?
MIC assays will increase in the presence of beta-lactamase and decrease in the presence of inhibitors. Using a substance such as potassium clavulanate, for example, as a negative control in combination with a beta-lactamase-producing bacteria or enzyme can establish the activity to observe for in the MIC assay for the substance combined with the same source for beta-lactamase.How I detect for beta lactamase?
IPTG induction in order to elicit beta-lactamase expression is recommended as well as determining if beta-lactamase is soluble. The cells should be lysed to extract the contents. Freeze-thawing the pellet and adding lysozymes may help in eradicating unnecessary material from the protein in interest. Ultracentrifuge the extract and run the supernatant using SDS-PAGE. The beta-lactamase protein, if it was initially expressed with a successful lysis and the being soluble in the solution, should appear as a band on SDS-PAGE.Beta-Lactamase Applications
-
Testing Sterility of Blood Cultures: Blood cultures are routinely prepared in order to test for bacterial infection. False negative results might be obtained where the blood sample contains antibiotics. Incorporation of β-Lactamase in the culture medium will overcome this problem when cephalosporins/penicillins are present.
-
Testing for Contamination of Drugs by Antibiotics: US Code of Federal regulations states that “If a reasonable possibility exists that a non-penicillin drug product has been exposed to cross-contamination with penicillin, the non-penicillin drug product shall be tested for the presence of penicillin” (21 CFR 211.176, Penicillin Contamination, FDA, BY-Lines No. 8 November 1977).
-
Environmental Monitoring: Monitoring within antibiotic manufacturing areas
-
Sterility Testing of Bulk Antibiotics: As described by US Pharmcopeia (USP) Chapter 71 and EP Section 2.6
Additional Reading
Beta-Lactamase and Microbial Antibiotic ResistanceBeta-Lactamase Composition, Sterility & Stability
Beta-Lactamase Inhibitors in Anti-Seizure Research
