LY294002 is a morpholine derivative of quercetin. It is a potent inhibitor of phosphoinositide 3-kinases (PI3Ks). PI3Ks (phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases) is an enzyme implicated in growth factor signal transduction by associating with receptor and nonreceptor tyrosine kinases, including the platelet-derived growth factor receptor. Inhibitors of PI3Ks could potentially give a better understanding of the function and regulatory mechanisms of the enzyme. The PI3Ks regulate cellular signaling networks that are involved in processes linked to the survival, growth, proliferation, metabolism and specialized differentiated functions of cells. The subversion of this network is common in cancer and has also been linked to disorders of inflammation. The elucidation of the physiological function of PI3K has come from pharmacological studies, which use the enzyme inhibitors Wortmannin and LY294002, and from PI3K genetic knockout models of the effects of loss of PI3K function.
LY294002 is a morpholine derivative of quercetin. It is a potent inhibitor of phosphoinositide 3-kinases (PI3Ks). PI3Ks (phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases) is an enzyme implicated in growth factor signal transduction by associating with receptor and nonreceptor tyrosine kinases, including the platelet-derived growth factor receptor. Inhibitors of PI3Ks could potentially give a better understanding of the function and regulatory mechanisms of the enzyme. The PI3Ks regulate cellular signaling networks that are involved in processes linked to the survival, growth, proliferation, metabolism and specialized differentiated functions of cells. The subversion of this network is common in cancer and has also been linked to disorders of inflammation. The elucidation of the physiological function of PI3K has come from pharmacological studies, which use the enzyme inhibitors Wortmannin and LY294002, and from PI3K genetic knockout models of the effects of loss of PI3K function.PI3Ks (phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases) 4 main fuctions
- Cell growth - The PI3K pathway is multi-stepped and complicated. It involves genes and proteins that cascade along chains of biochemical events. But the underlying premise is straightforward. PI3K adds phosphates onto a lipid in the cell membrane. Once phosphorylated, these lipids act as messengers recruiting cellular machinery needed to communicate growth and survival signals to the cell.
- Proliferation - The pan-inhibitor of PI3Ks LY294002 is able to abrogate the TGF-Beta-induced increase in cell proliferation, in smooth muscle actin expression and in collagen production besides inhibiting Akt phosphorylation, thus demonstrating the centrality of the PI3K/Akt pathway in lung fibroblast proliferation and differentiation.
- Differentiation - The signaling pathways mediating human intestinal epithelial cell differentiation remain largely undefined. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) is an important modulator of extracellular signals, including those elicited by E-cadherin-mediated cell-cell adhesion, which plays an important role in maintenance of the structural and functional integrity of epithelia.
- Motility - PI3K, PTEN and localized phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate [PtdIns(3,4,5)P3] play key roles in chemotaxis, regulating cell motility by controlling the actin cytoskeleton in Dictyostelium and mammalian cells.
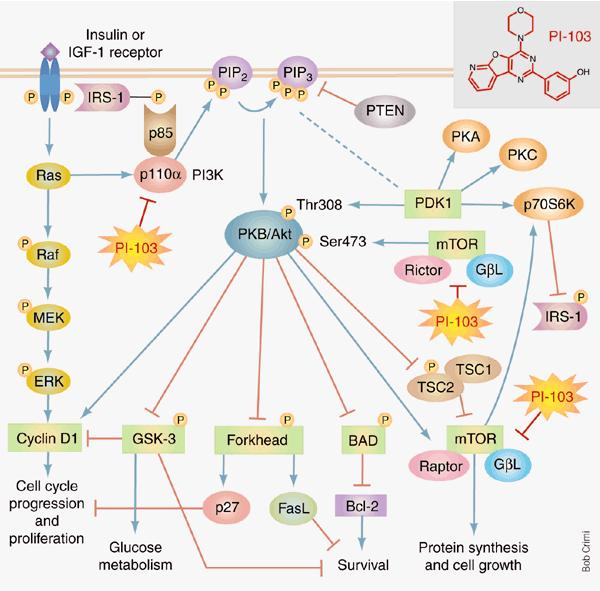
Figure 1: PIK pathway and related pathways
