Here is a list of the Top 10 Deadliest Diseases in the World affecting humans. The information presented here has bee compiled via the World Health Organization's (WHO) reported data as of 2012.
10. Preterm Birth Complications
Although not a disease, an estimated 1 million infants are lost to due to pre-maturity and low birth weight. Most deaths occur after the first week of conceiving. These complications mostly affect developing countries where medical care is not available or is difficult to reach. The WHO estimates that PBC contributes to about 1.8% of all deaths.
9. Diabetes Mellitus

Diabetes Mellitus Type I is characterized by the pancreatic cells no longer or miniscully producing insulin or the production is miniscule. In type II diabetes, cells lose sensitivity to insulin, thereby becoming resilient. Type I diabetes cannot be cured, but type II diabetes can be maintained with a proper diet and exercise. An estimated 1.26 million people have lost their lives to complications with diabetes in 2012, which contributes to about 2.2% of all deaths.
8. Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is a bacterial infection caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Contraction of TB is airborne, but it is difficult to get. It is one of the leading causes of death for people coupled with HIV. An estimated 1.34 million people died from TB in 2012, contributing to about 2.4% of all deaths.
7. Respiratory Cancers
This class of diseases include lung, tracheal, and bronchial cancers. The main cause of these cancers are pollution by smoking, secondhand smoking, and other carcinogens as a waste byproduct. An estimated 1.39 million people died in 2012 from respiratory cancers which contributes to about 2.4% of all deaths.
6. HIV/AIDS
AIDS is caused by the Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) which is transmitted through bodily fluids. HIV enters the body and hijacks T cells which then compromises the immune system. In 2012, about 1.78 million people died due to AIDS. This contributes to about 3.1% of all deaths. It is estimated that over 5000 people become infected every day.
5. Diarrheal Diseases

Diarrhea is characterized by excreting fecal matter more than three times a day. Having diarrhea over the course of a few days depletes the body of water and salt. The WHO estimates that diarrheal diseases has claimed 2.46 million lives in 2012. It is the second leading cause of death of children under 5. This contributes to about 4.3% of all deathsglobally.
4. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)

This disease affects the lungs, making it more difficult for the patient to breathe. The main cause of COPD is tobacco use, including second hand smoke. The WHO estimates that COPD has claimed 3.28 million lives in 2012, which contributes to about 5.8% of all deaths worldwide.
3. Lower Respiratory Infections (LRI)
LRI includes influenza, bronchitis, and pneumonia. The flu season is mostly prevalent in the colder half of the year for each hemisphere. The WHO estimates that LRI contributes to about 6.1% of all deaths.
2. Stroke
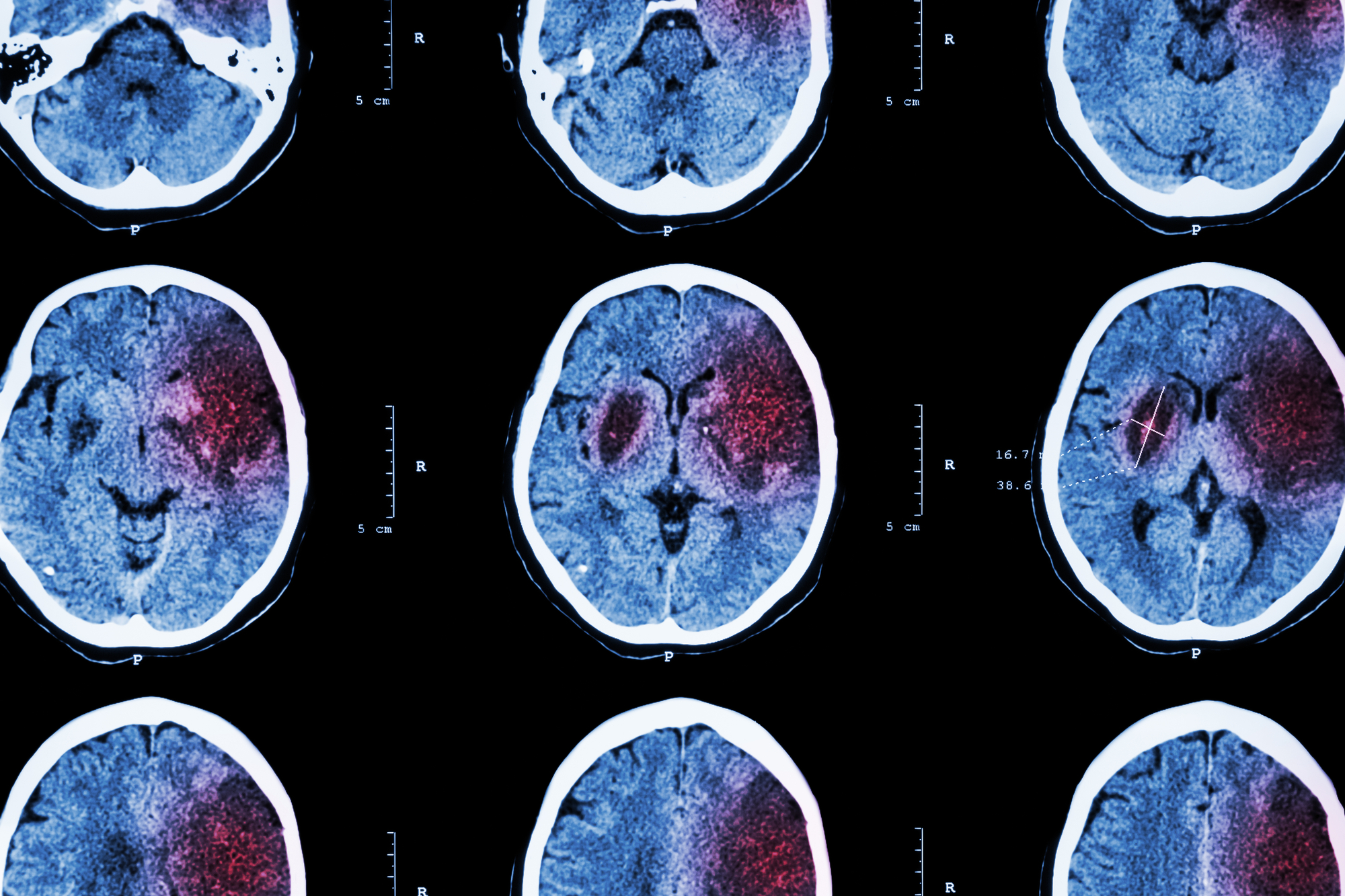
A stroke occurs when an artery supplying blood to the brain is blocked or leaked. The oxygen-deprived cells die within minutes of the blockage. According to WHO, an estimated 6.7 million lives are lost to strokes in 2012. This contributes to about 10.8% of all deaths.
1. Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
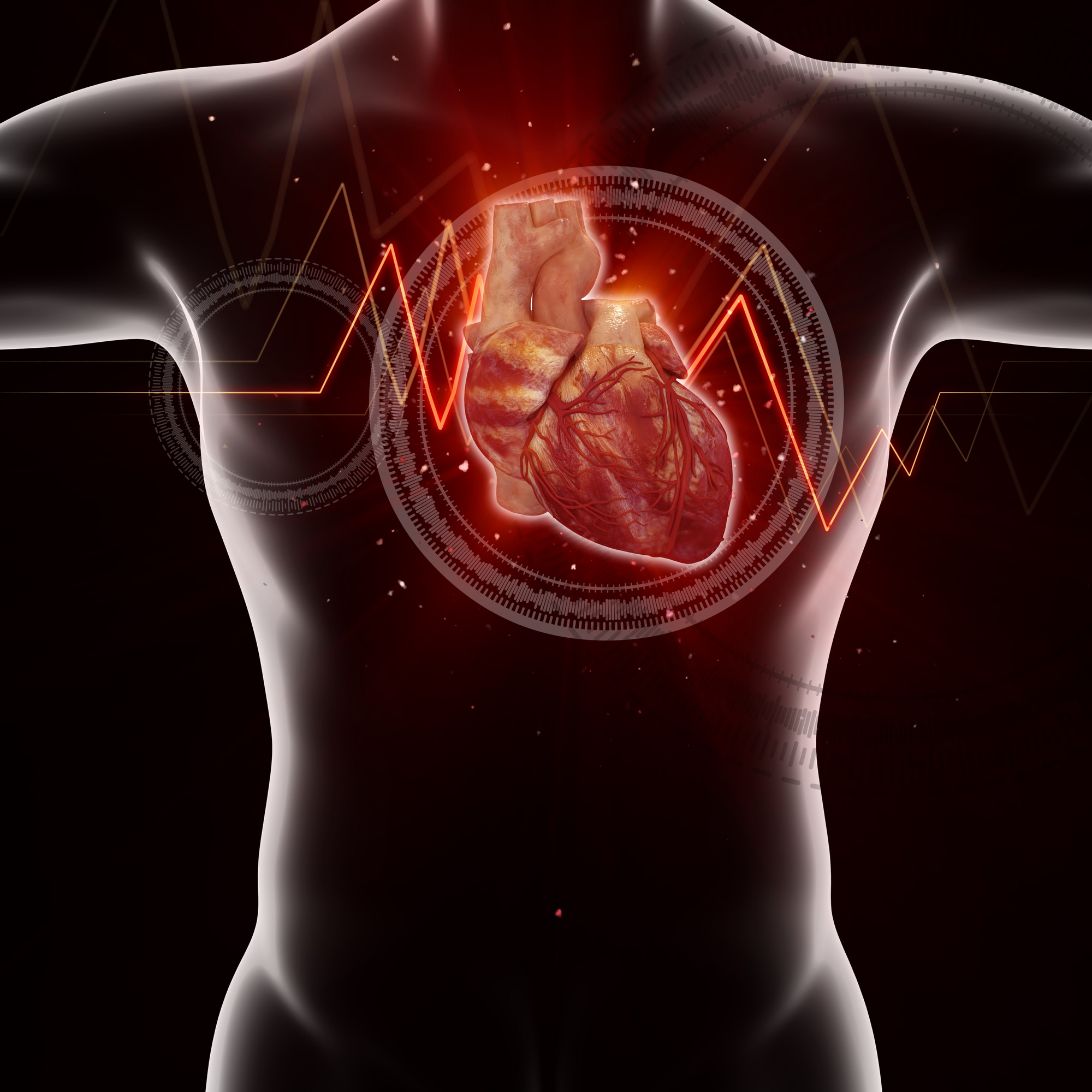
CAD is a condition where vessels supplying blood to the heart become narrowed. This is commonly caused by unhealthy dieting and smoking. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that CAD has claimed about 7.4 million lives in 2012. That contributes to about 12.8% of all deaths globally.




