MECHANISM OF ACTION: epirubicidin, anthracycline, antibiotics, anticancerThe mechanism of action of epirubicin appears to be related to its ability to bind to nucleic acids. It forms a complex with DNA by intercalation between base pairs, resulting in inhibition of DNA and RNA synthesis. Intercalation also triggers DNA cleavage by topoisomerase II, resulting in cytocidal activity.
MECHANISM OF ACTION: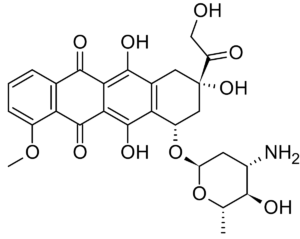
The mechanism of action of
epirubicin appears to be related to its ability to bind to nucleic acids. It forms a complex with DNA by intercalation between base pairs, resulting in inhibition of DNA and RNA synthesis. Intercalation also triggers DNA cleavage by topoisomerase II, resulting in cytocidal activity. Binding to cell membranes and plasma proteins may also be involved.
Epirubicin also generates cytotoxic free radicals. Epirubicin is the 4-epimer of
DOXOrubicin; i.e., there is a different spatial orientation of the hydroxyl group at the 4 carbon of the sugar moiety. This difference may account for faster elimination and reduced toxicity.
SYNONYM(S): 4-epidoxorubicin, IMI-28, NSC-256942
COMMON TRADE NAME(S): PHARMORUBICIN®, ELLENCE®
CLASSIFICATION: anthracycline antineoplastic antibiotic
PHARMACOKINETICS
Primary Uses
| Breast Cancer |
Gastric Cancer |
| Lung Cancer, non small cell |
Lung Cancer, small cell |
| Lymphoma |
Ovarian Cancer |
Other Uses
| Bladder Cancer |
Pediatric, soft tissue sarcoma |
Soft tissue Sarcoma |

