Aristolochiaceae are a flowering plants family, with about 500 species. Other common names are birthworts, pipevines or dutchman's pipes. hese medicines are use as anti-inflammatory and slimming agents, diuretics and in the treatment of oedema, coughs, phlegm, wheezing, hypertension, dizziness, bleeding hemorrhoids, etc .
Herb carcinogen, aristolochic acid, causes higher mutation-rate than smoke or UV.
| Aristolochiaceae are a flowering plants family, with about 500 species. Other common names are birthworts, pipevines or dutchman's pipes. The pipe names are an allusion to old-fashioned meerschaum pipes, similar to the flower shape of this plants and birthwort refers to the function of these flowers as birth canal for some insects , e.g. Pipevine Swallowtail, a swallowtail butterfly found in North America and Central America. There are herbaceous plants, which can become either shrub, woody vines or even lianas.The plants of the genus Aristolachia are very common and widespread in the most diverse climates. They occur along the banks of canals, edges of ditches and fields, sides of roads, meadows, slopes and forests. It is common for children to pick them up because of their beautiful deep purple color and funny shape. Nowadays, these plants are known for their toxicity. |

Clockwise from the top-left corner, Aristolochia elegans, Aristolochia Californica, Aristolochia baetica and Aristolochia fimbriata
These plants have been used since the Egyptians and Greeks, but especially in traditional Chinese medicine. On the left, there is a table distinguishing each the Aristolachia species, and which part is used for medicine in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia. These medicines are use as anti-inflammatory and slimming agents, diuretics and in the treatment of oedema, coughs, phlegm, wheezing, hypertension, dizziness, bleeding hemorrhoids, etc. Because of this antiquity, as well as other ancients medicine, nobody has ever wondered about the possible adverse effects that may result from these medicines.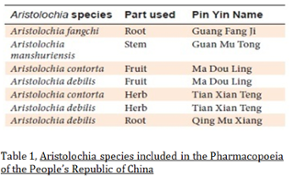 The first conjecture of this poisonous was during 1990-1992. A Belgium clinic prescribed a Chinese herbal weight-loss remedy for a woman, who after being treated, developed kidney problems that progressed into renal failure and, in later years, to abnormal growths in her upper urinary tracts: a disorder was called aristolochic acid nephropathy (AAN). More recently, Aristolochia contamination of local wheat crops was determined to be the cause of a high incidence of urothelial carcinomas of the upper urinary tract (UTUC) among rural communities on the banks of the Danube river in Europe.In Taiwan, recent prescription records reveal that approximately one-third of the population has taken Aristolochia-containing medicines; the highest incidence of UTUCs in the world.
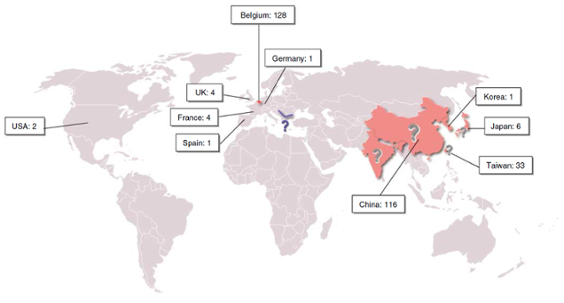
The first conjecture of this poisonous was during 1990-1992. A Belgium clinic prescribed a Chinese herbal weight-loss remedy for a woman, who after being treated, developed kidney problems that progressed into renal failure and, in later years, to abnormal growths in her upper urinary tracts: a disorder was called aristolochic acid nephropathy (AAN). More recently, Aristolochia contamination of local wheat crops was determined to be the cause of a high incidence of urothelial carcinomas of the upper urinary tract (UTUC) among rural communities on the banks of the Danube river in Europe.In Taiwan, recent prescription records reveal that approximately one-third of the population has taken Aristolochia-containing medicines; the highest incidence of UTUCs in the world.
The harm compound of the Aristolachia genus plants is the aristolochic acid (AA). This term refers to an extract of Aristolochia species comprising of a mixture of aristolochic acid I and its demethoxylated derivative, aristolochic acid II. This compound has been reported to function as a phospholipase A2 inhibitor, antiseptic, anti-inflammatory and bactericidal agent.
-Structural and Molecular formula of aristolachia acid: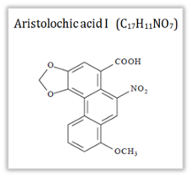 |
-Synonyms: Aristolochia yellowAristinic acid Aristolochic acid A Aristolachin Aristolochine Descresept Isoaristolachic acid | -Chemistry name:
8-Methoxy-6-nitrophenanthro[3,4-d]-1,3-dioxole-5-carboxylic acid8-Methoxy- 6-nitronaphtho[2,1-g][1,3] benzodioxole- 5-carboxylic acid
8-methoxy-3,4-methylenedioxy-10-nitrophenanthrene-1-carboxylic acid
3,4-methylenedioxy-8-methoxy-10-nitro-1-phenanthrenecarboxylic acid
|
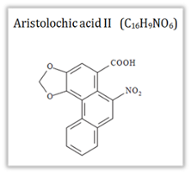 |
Aristolochic acid B | 6-Nitrophenanthro[3,4-d]-1,3-dioxole-5-carboxylic acid6-Nitronaphtho[2,1-g][1,3]benzodioxole-5-carboxylic acid3,4-methylenedioxy-10-nitrophenanthrene-1-Â carboxylic acid |
The major activation pathway of aristolochic acids involves reduction of the nitrogroup. During this process, AA forms an electrophilic cyclic N-acylnitrenium ion that reacts with purine bases to form DNA adducts.
Two different studies experimented on the carcinogenic effects of AA. At first, they tested the action of AA putting it together with renal tubular human cells, and it resulted in a high number of transversion A:T to T:A mutations. The cause of this transversion may have been due to the DNA adducts explained before. Afterwards, the researchers used different experimental animals (rats, mice, and rabbits) to analyze the different vias of how AA provokes abnormal growth. They administered either orally, intravenously, intraperitonal or subcutaneal, and all of the assay showed development of tumors in different organs (e.g. forestomach tumours, kidney adenomas and lung carcinomas). The aristolochic- acid-specific DNA adducts have been identified and detected in these experimental animals as well. Besides that, both studies carried out several carcinoma screening at UTUC-individuals supposed to be treated with Archilochia related medicines, the RNA analysis showed the high frequency of A:T to T:A mutation, most in a A[C|T] AGG context, affecting specifically at the KDM6A, a histone demethylase gene. The conclusion was that this genotoxic substance causes the transversion mutation, which characterizes the urothelial carcinomas of UTUC.
 The effect of the mutation at KDM6A, provokes an up-regulation of non-sense mediated decay (NMD) machinery component, detected at the quantitative reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR) and aberrant splicing events associated with splice-site mutations.
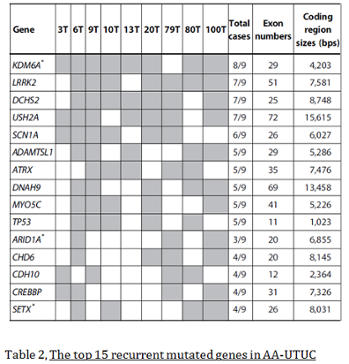
The research explains that the transversion firstly occurs in nontranscripted strands of DNA and, in later time, it happens at the splice sites, specifically KDM6A. But on the Table1 of the article: Genome-Wide Mutational Signatures of Aristolochic Acid and Its Application as a Screening Tool, there is a list of the other genes which are less but even though affected at the UTUC.
Until now occupational dermal exposure to AA has not been documented. Herbalists are potentially exposed while gathering plants or while preparing or applying botanical products, that could result in dermatitis. To reduce the likelihood of accidental ingestion, workers should wash their hands before eating, drinking, or smoking.
The highlights of these researches are:
1) Aristolochic acids are consistently active in genotoxicity tests in vivo and in vitro.
2) Unusual genome-wide, determine the AA mutational signature.
3) Use of AA mutational signature as molecular fingerprint to enable early detection of UTUCs.
4) The evidence of the existence of natural substances with higher carcinogenic effects than tobacco or UV. AA provokes a strikingly high somatic mutation rate 150 mutations/Mb; much more than smoking-associated lung cancer (8 mutations/Mb) or UV radiation-associated melanoma (111 mutations/Mb).
Aristolochic acid has been prevented of consuming in most countries since 2003, but there are a lot of countries in Asia, like India, that are still using it as part of their traditional herbal medicines. Even though it is banned in places like China, it is still easily available. For doctors are slow to accept that they are hurting people who they are trying to help. This fact may be supported due to the fact that the time between the treatments with AA until the development of the tumor, could last until 20 years.
References
The effect of the mutation at KDM6A, provokes an up-regulation of non-sense mediated decay (NMD) machinery component, detected at the quantitative reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR) and aberrant splicing events associated with splice-site mutations.
The research explains that the transversion firstly occurs in nontranscripted strands of DNA and, in later time, it happens at the splice sites, specifically KDM6A. But on the Table1 of the article: Genome-Wide Mutational Signatures of Aristolochic Acid and Its Application as a Screening Tool, there is a list of the other genes which are less but even though affected at the UTUC.
Until now occupational dermal exposure to AA has not been documented. Herbalists are potentially exposed while gathering plants or while preparing or applying botanical products, that could result in dermatitis. To reduce the likelihood of accidental ingestion, workers should wash their hands before eating, drinking, or smoking.
The highlights of these researches are:
1) Aristolochic acids are consistently active in genotoxicity tests in vivo and in vitro.
2) Unusual genome-wide, determine the AA mutational signature.
3) Use of AA mutational signature as molecular fingerprint to enable early detection of UTUCs.
4) The evidence of the existence of natural substances with higher carcinogenic effects than tobacco or UV. AA provokes a strikingly high somatic mutation rate 150 mutations/Mb; much more than smoking-associated lung cancer (8 mutations/Mb) or UV radiation-associated melanoma (111 mutations/Mb).
Aristolochic acid has been prevented of consuming in most countries since 2003, but there are a lot of countries in Asia, like India, that are still using it as part of their traditional herbal medicines. Even though it is banned in places like China, it is still easily available. For doctors are slow to accept that they are hurting people who they are trying to help. This fact may be supported due to the fact that the time between the treatments with AA until the development of the tumor, could last until 20 years.
References
- Wikipedia-Aristolochia
- Wikipedia-Aristolochia rotunda
- Whole Foods Harmony Market
- Cancer-Causing Herbal Remedies
- Aristolochic acid nephropathy: A worldwide problem, 2008, International Society of Nephrology, Frederic D. Debelle,et al.
- Upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma: what have we learned in the last 4 years?, 2011, Ther Adv Urol., Mesut Remzi, et al.
- Plants containing aristolochic acid, IARC Working Group, 2002
- Genome-wide mutational signatures of aristolochic acid and its application as a screening tool, 2013, Sci. Transl. Med., Song Ling Poon, et al.
Image Sources
