The PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway is central to cell growth and survival, cell cycle regulation, and programmed cell death.Aberrant activation of this signaling cascade is linked to several disease states, and thus many components of the pathway are attractive targets for therapeutic intervention.
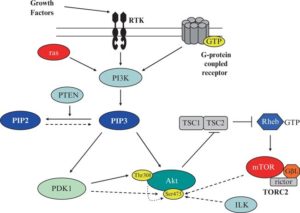
Figure 1. PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway.
Akt is a crucial kinase in this pathway that is activated by phosphorylation in the activation domain (T308) and in the hydrophobic motif (S473). Once active, Akt exerts its cellular effects through the phosphorylation of downstream substrates that regulate the apoptotic machinery, cell cycle progression, gene expression, metabolism, and protein translation. Of all downstream Akt substrates, mTOR is probably the best studied, perhaps due to the availability of drugs that specifically inhibit mTOR.
Is PI3K/Akt/mTOR Pathway Important in Many Types of Cancer?
Yes. The measurement of active Akt and other pathway components in human tumors has revealed that pathway activation is one of the most common molecular alterations in human cancer. Using activation state specific antibodies in immunohistochemical (IHC) analyses of paraffin-embedded, formalin-fixed tissues, active Akt and other pathway components have been detected in at least 12 types of human cancers in vivo, with prevalence as high as 90%.The importance of pathway activation in situ has been demonstrated when IHC analysis of tumor tissues has been linked to clinical outcomes. Akt activation is a poor prognostic factor for breast cancer, prostate cancer, non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), endometrial cancer, gastric cancer, pancreatic cancer, glioblastoma multiforme, melanoma, and acute myelogenous leukemia. Thus, constitutive activation of this pathway is common and important in many cancers.
Pathway Inhibitors Prevent Cancer in Preclinical Model Systems
Although pathway inhibitors that target individual components such as PI3K, PDK-1, Akt, and mTOR are being developed, mTOR inhibitors are the most mature. mTOR inhibitors include rapamycin, which is FDA-approved as an immunosuppressant, and analogues such as RAD001 and CCI779 that are in late phase clinical trials with cancer patients. mTOR inhibitors have been effective in preclinical models of lung tumorigenesis, breast tumorigenesis, and prostate tumorigenesis.AG Scientific's Toll-Like Receptor (TLR) Signaling Products
|
E-2044
|
Irreversible Inhibitor of Neutrophil and rat microglia elastase. Inhibits proteolytic activity of poliovirus and rhinovirus 2A proteinases. Primary target: elastase-like serine protease. | |
|
|
I-2361
|
Cell-permeable. Topical immune response modifier that displays anti-angiogenic, anti-viral and anti-inflammatory properties. Up-regulates IL-18 and down-regulates MMP-9 through recognition of Toll-like receptor 7 (TLR7) and subsequent activation of MyD88-dependent pathway. |
|
N-1171
|
Nystatin is an antifungal agent produced from Streptomyces sp. It exhibits fungicidal and fungistatic activity. Mode of Action: Increases the permeability of the cell membrane of sensitive fungi by binding to sterols. | |
|
P-2378
|
A synthetic triacylated lipopeptide (LP) that mimics the acylated amino terminus of bacterial LPs. Pam3CSK4 is a potent activator of the proinflammatory transcription factor NF-kB. Activation is mediated by the interaction between Toll-like receptor 1 (TLR1) and Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2). | |
|
|
R-2416
|
A selective ligand for Toll-like receptor 7 (TLR7) in mouse and for TLR7 and TLR8 in humans. Displays antitumor and antiviral properties. Stimulates antibody secretion, cytokine production. |

