Combined treatment with a proteasome inhibitor and tumor necrosis factor–related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) is a promising strategy for cancer therapy.
Introduction
 Combined treatment with a proteasome inhibitor and tumor necrosis factor related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) is a promising strategy for cancer therapy.
Proteasome inhibitors induce the expression of death receptor 5 (DR5), a receptor for TRAIL, and sensitize cancer cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis; however, the molecular mechanism of DR5 up-regulation has not been elucidated. In this study, we report that CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein homologous protein (CHOP) is a regulator of DR5 induction by proteasome inhibitor MG132. MG132 induced DR5 expression at a protein and mRNA level in prostate cancer DU145 cells. Furthermore, MG132 increased DR5 promoter activity. Using a series of deletion mutant plasmids containing DR5 promoters of various sizes, we found that MG132 stimulated the promoter activity via the region of 289 to 253. This region contained a CHOP-binding site. Site-directed mutation of the site abrogated the promoter activity enhanced by MG132. An electrophoretic mobility shift assay showed that CHOP directly bound to the MG132-responsive site on the DR5 promoter. Expression of the CHOP protein was increased with MG132 along with DR5 up-regulation. Furthermore, CHOP small interfering RNA attenuated the DR5 up-regulation due to MG132. These results indicate that the proteasome inhibitor MG132 induces DR5 expression through CHOP up-regulation.
Combined treatment with a proteasome inhibitor and tumor necrosis factor related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) is a promising strategy for cancer therapy.
Proteasome inhibitors induce the expression of death receptor 5 (DR5), a receptor for TRAIL, and sensitize cancer cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis; however, the molecular mechanism of DR5 up-regulation has not been elucidated. In this study, we report that CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein homologous protein (CHOP) is a regulator of DR5 induction by proteasome inhibitor MG132. MG132 induced DR5 expression at a protein and mRNA level in prostate cancer DU145 cells. Furthermore, MG132 increased DR5 promoter activity. Using a series of deletion mutant plasmids containing DR5 promoters of various sizes, we found that MG132 stimulated the promoter activity via the region of 289 to 253. This region contained a CHOP-binding site. Site-directed mutation of the site abrogated the promoter activity enhanced by MG132. An electrophoretic mobility shift assay showed that CHOP directly bound to the MG132-responsive site on the DR5 promoter. Expression of the CHOP protein was increased with MG132 along with DR5 up-regulation. Furthermore, CHOP small interfering RNA attenuated the DR5 up-regulation due to MG132. These results indicate that the proteasome inhibitor MG132 induces DR5 expression through CHOP up-regulation.
 MG132 enhances tumor necrosis factor related apoptosis-inducing ligand induced apoptosis in DU145 cells
We examined the effect of combined treatment with proteasome inhibitor MG132 and TRAIL on apoptosis by measuring the sub-G1population. MG132 or TRAIL slightly induced apoptosis as single agents in prostate cancer DU145 cells; however, combined treatment with MG132 and TRAIL markedly induced apoptosis.
MG132 induces death receptor 5 expression in DU145 cells
Next, we examined DR5 up-regulation by MG132. First, we carried out Western blotting to investigate the induction of DR5 protein by MG132. MG132 increased DR5 protein in a dose-dependent manner (Fig. 1A). We examined whether MG132 regulated DR5 expression at an mRNA level. DR5 mRNA was also remarkably increased by MG132 treatment (Fig. 1B). These results indicated that MG132 up-regulates DR5 expression at an mRNA and protein level in DU145 cells.
Identification of MG132-responsive elements in the death receptor 5 promoter
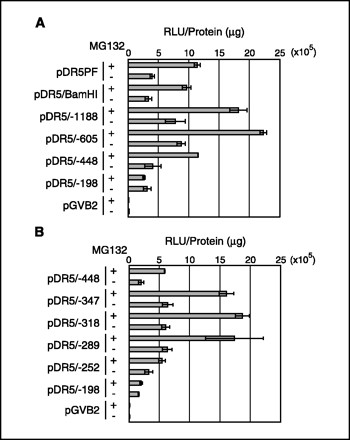
To elucidate the mechanism of the DR5 up-regulation by MG132, we carried out a luciferase assay using reporter plasmids containing the DR5 promoter. MG132 increased the promoter activity of pDR5PF, a luciferase reporter plasmid containing an 2.5-kbp fragment of the DR5 promoter region (Fig. 2A). This result indicated that MG132 regulates DR5 expression through transcription. Using a series of 5-deletion mutants, we investigated the MG132-responsive elements on the DR5 promoter. pDR5/448 but not pDR5/198 was activated by MG132 (Fig. 2A). Therefore, we generated 5-deletion mutants between 448 and 198 and did the luciferase assay. As shown in Fig. 2B, the MG132-responsive element seemed located in a 37-bp region between 289 and 253 in the DR5 promoter, although we can not rule out the possibility that other responsive regions might also exist.
Sources: Tatsushi Yoshida, Takumi Shiraishi, Susumu Nakata, Mano Horinaka, Miki Wakada, Yoichi Mizutani, Tsuneharu Miki, and Toshiyuki Sakai
MG132 enhances tumor necrosis factor related apoptosis-inducing ligand induced apoptosis in DU145 cells
We examined the effect of combined treatment with proteasome inhibitor MG132 and TRAIL on apoptosis by measuring the sub-G1population. MG132 or TRAIL slightly induced apoptosis as single agents in prostate cancer DU145 cells; however, combined treatment with MG132 and TRAIL markedly induced apoptosis.
MG132 induces death receptor 5 expression in DU145 cells
Next, we examined DR5 up-regulation by MG132. First, we carried out Western blotting to investigate the induction of DR5 protein by MG132. MG132 increased DR5 protein in a dose-dependent manner (Fig. 1A). We examined whether MG132 regulated DR5 expression at an mRNA level. DR5 mRNA was also remarkably increased by MG132 treatment (Fig. 1B). These results indicated that MG132 up-regulates DR5 expression at an mRNA and protein level in DU145 cells.
Identification of MG132-responsive elements in the death receptor 5 promoter
To elucidate the mechanism of the DR5 up-regulation by MG132, we carried out a luciferase assay using reporter plasmids containing the DR5 promoter. MG132 increased the promoter activity of pDR5PF, a luciferase reporter plasmid containing an 2.5-kbp fragment of the DR5 promoter region (Fig. 2A). This result indicated that MG132 regulates DR5 expression through transcription. Using a series of 5-deletion mutants, we investigated the MG132-responsive elements on the DR5 promoter. pDR5/448 but not pDR5/198 was activated by MG132 (Fig. 2A). Therefore, we generated 5-deletion mutants between 448 and 198 and did the luciferase assay. As shown in Fig. 2B, the MG132-responsive element seemed located in a 37-bp region between 289 and 253 in the DR5 promoter, although we can not rule out the possibility that other responsive regions might also exist.
Sources: Tatsushi Yoshida, Takumi Shiraishi, Susumu Nakata, Mano Horinaka, Miki Wakada, Yoichi Mizutani, Tsuneharu Miki, and Toshiyuki Sakai