Ansamycins is a family of secondary metabolites that show antimicrobial activity against many gram-positive and some gram-negative bacteria and includes various compounds, among which: streptovaricins and rifamycins. In addition, these compounds demonstrate antiviral activity towards bacteriophages and poxviruses.
Ansamycins is a family of secondary metabolites that show antimicrobial activity against many gram-positive and some gram-negative bacteria and includes various compounds, among which: streptovaricins and rifamycins. In addition, these compounds demonstrate antiviral activity towards bacteriophages and poxviruses. They are named ansamycins (from the Latin ansa, handle) because of their unique structure, which comprises an aromatic moiety bridged by an aliphatic chain. The main difference between various derivatives of ansamycins is the aromatic moiety, which can be a naphthalene ring or a naphthoquinone ring as in rifamycin and naphthomycins. Another variation comprises benzene or a benzoquinone ring system as in geldanamycin or ansamitocin.The ansamycin family of natural products and their derivatives, such as Geldanamycin (GA) are well-known inhibitors of the essential ATPase activity of Heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90). Hsp90 is a molecular chaperone that is required for the maturation and activation of a number of client proteins, many of which are involved in cancer development. Hsp90 inhibitors include the natural products geldanamycin and radicicol as well as semisynthetic derivatives 17-N-Allylamino-17-demethoxygeldanamycin (17AAG), 17-DMAG.
Benzoquinonoid ansamycin antibiotics were first isolated in the late 1970s from the culture broths of several actinomycete species. Considerable interest was generated by their unusual ansa bridge structure, and a number of compounds including Herbimycin A (HB) and Geldanamycin (GA) were screened as possible anstiretroviral and antitumor agents. The benzoquinoid antibiotics, the mactecins, the herbrimycins, and geldanamycin, are representative of an emerging class of ansa-bridged marcrocyclic lactams possessing a significant range of antitumor activity. Recent studies have indicated that the benzoquinoid ansamycins, specifically the herbmycins, have antitumor functions. In addition to reversing the characteristics of oncogene expression, herbimycin A has been shown to have potent antiangiogenic activity. This latter biological activity distinguishes the benzoquinoid ansamycins from their benzenoid and naphthoquinoid ansamycin relatives. Source: Luke whitesell, Stuart D. Shifrin, Gisela Schwab, et al. Benzoquinonoid Ansamycins Possess Selective Tumoricidal Activity Unrelated to src Kinase Inhibition, Onuoha SC, Mukund SR, et al. Mechanistic studies on Hsp90 inhibition by ansamycin derivatives, David A Evans, Scott J.Miller, et al. Asymmetric Synthesis of of the Benzoquinoid Ansamycin Antitumor Antibiotics: Total Synthesis of (+)-Macbecin, Wikipedia.
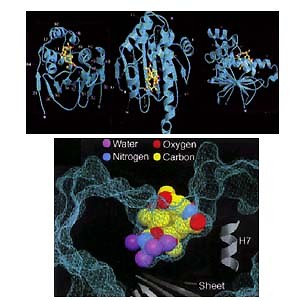
Figure 2: Crystal structure of geldanamycin bound to Hsp90.
BENZOQUINONOID ANSAMYCINS ANTIBIOTIC EXAMPLES:
|
Macbecin |
|
|
Naphthomycin |
|
|
Ansatrienin(mycotrienin) |
|
|
Awamycin |
|
|
Ansathiazin |
Macbecin I |

