PMSF (phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride) is an irreversible serine protease inhibitor used in various research and lab settings. The compound has a white powdery appearance at room temperature, with a melting point between 90-95°C. It functions by inhibiting serine proteases such as trypsin, chymotrypsin, and thrombin, and cysteine proteases like papain.
The process involves the deactivation of enzymes that contain serine on its active sites through esterification. Serine proteases naturally exist within all organisms and are responsible for a wide range of biological processes. For example, trypsin and elastase serve as pancreatic digestive enzymes, while fibrinolysin affects cell transformation. Compounds such as PMSF can help researchers preserve pure cell samples from the lab by protecting against the enzymatic functions of proteases.
This inhibitor has limited solubility, which requires researchers to dissolve the compound in a solvent such as ethanol, methanol, or isopropanol before use. As such, it may serve as an alternative to water-soluble protease inhibitors such as AEBSF (4-benzenesulfonyl fluoride hydrochloride). Due to its short half-life (usually only lasting between cell lysis and the first step of purification), researchers may consider applying other protease inhibitors to prolong the enzymes’ biological activity for their research needs.
Common Applications
Preparation of Cell Lysates
Lysis is a process that involves the break down of cell membranes, which can facilitate detailed research on cell compositions. The results of lysis are known as lysates. Researchers studied PMSF as an inducer of enzymatic activities in the stimulation of wood degradation (cherry sawdust) by fungal species (Daedaleopsis confragosa and D. tricolor). The research suggests the vital role of PMSF in lysis preparations, in the case of ligninolytic enzymes. PMSF can help researchers prepare cell lysates with accuracy, ensuring enzymatic reactions do not compromise target proteins by interacting through a lysate buffer. For example, scientists often add PMSF to the lysate buffer to prepare cell lysates from E.Coli. Researchers applied PMSF in the research of Sofalcone, a synthetic chalcone used as a protective agent for gastric mucus. The team included PMSF in the preparation of the lysate buffer, tissue extracts, tissue lysates, and tissue nuclear extracts. PMSF-use led researchers to discover the drug's function in binding with the KEAP1 protein, which results in anti- colitic effects.Sample Preservation
PMSF is used to deactivate specific proteins after lysis to provide a solubilized research sample. The non-specific nature of this inhibitor enables researchers to apply the compound to a variety of studies. For example, scientists used PMSF concentrations in studying the effects of anandamide in the Mouse Model of Cannabimimetic Activity. Researchers discovered that PMSF blocked the metabolic functions of anandamide, a major psychotropic constituent found in marijuana. PMSF provided researchers with access to the target compound. In another example, researchers studied the factors leading to the loss of bacteria in preserved seawater samples. By adding PMSF to glutaraldehyde (the preservative used in the experiment), scientists discovered the reduced loss of bacteria over a 30-35 day period. The experiment supported PMSF's role in preserving bacteria in glutaraldehyde-preserved samples.Protein Purification
The cellular levels of biological proteins are stable when left in their natural state or under moderated environmental conditions. In vitro studies and experiments will disrupt the cellular mechanics of proteins, leading to degradation and denaturing. A protease inhibitor such as PMSF will keep proteins stabilized or purified during research by mitigating enzymatic reactions. Specifically, during lysis, cells/organelles may face the disruption of regulatory mechanisms that normally inhibit protease reactions. The reaction leads to the break down of various proteins through proteolysis. As a result, researchers may lose proteins of interest in the process, which affects the accuracy of their findings. Researchers commonly apply PMSF and AEBSF to the protein purification process as most proteases in cells and tissues belong to the serine protease group. As such, PMSF is a crucial component in lysis buffers for serine-based experiments. The inclusion of PMSF reduces the contamination of samples due to enzymatic reactions and provides researchers with a larger concentration of functional proteins.Purchasing Quality Reagents & Compounds
Researchers may add PMSF to inhibitor cocktails or mixtures of protease inhibitors to provide lysate samples with comprehensive protection against the enzymatic effects of all four catalytic proteases: serine, cysteine, aspartic, and metallo. AG Scientific provides high quality PMSF for individual use, in combination with inhibitor cocktails, or for the needs of your customized formulations. We also offer a diverse inventory of additives for the preparation of lysis buffers.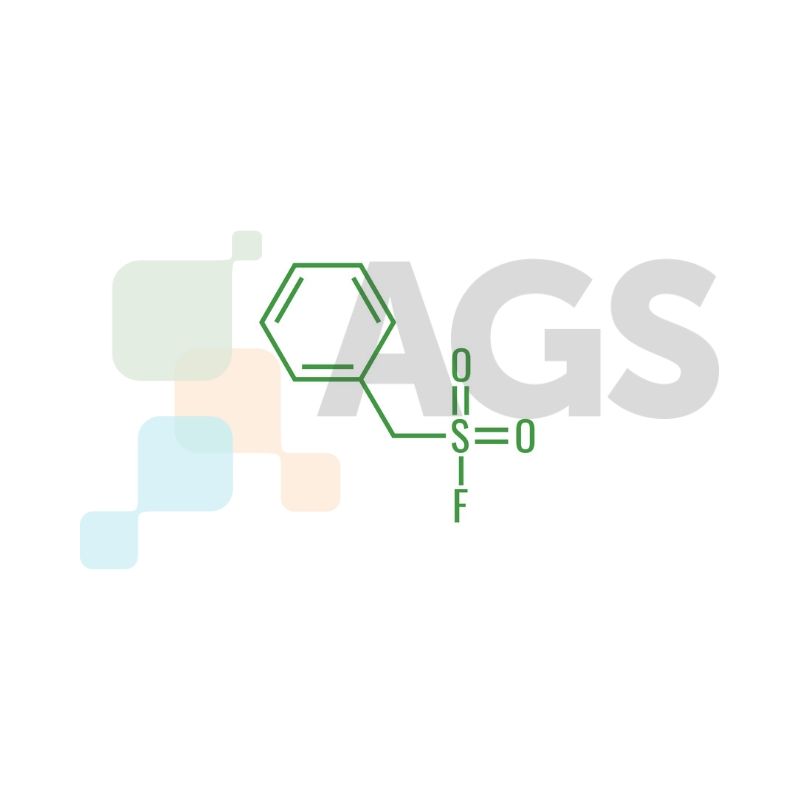
AG Scientific is the trusted supplier of premium scientific products for your lab and educational needs, including PMSF and AEBSF. Visit our site to learn more about our vast inventory of products as we remain your trusted ally in discovery.
Additional Reading
- PMSF: Frequently Asked Questions
- The SUnSET Assay: Powerful Proteomics
- Pathology Research Using Mitophagy Modulators

